
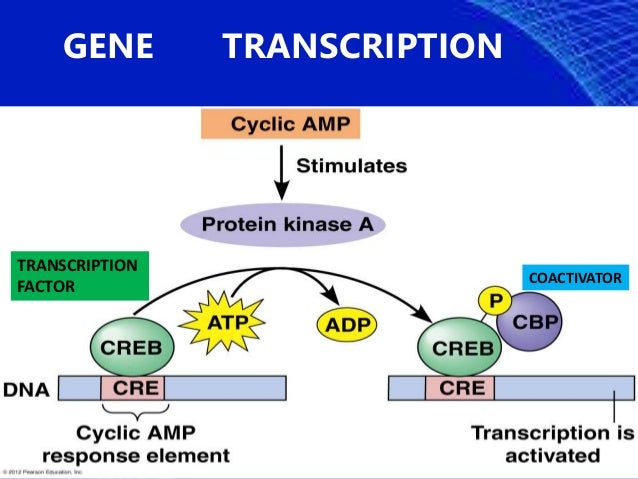
In this respect, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) signaling acts as a major modulator of fibrotic responses activated in fibroblasts of injured or stressed hearts. Despite the well-established role of myofibroblasts in mediating cardiac disease, our current knowledge on how signaling pathways promoting fibrosis are regulated and coordinated in this cell type is largely incomplete. Uncontrolled myofibroblast activation can thus promote heart stiffness, cardiac dysfunction, arrhythmias, and progression to heart failure. These activated fibroblasts display increased proliferative capacity and secrete large amounts of extracellular matrix. The fibrotic process is initially triggered by the differentiation of resident cardiac fibroblasts into myofibroblasts. Philadelphia (PA): AACR Cancer Res 2018 78(13 Suppl):Abstract nr 3548.Myocardial stress and injury invariably promote remodeling of the cardiac tissue, which is associated with cardiomyocyte death and development of fibrosis. In: Proceedings of the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2018 2018 Apr 14-18 Chicago, IL. EPAC-RAP1, the alternative cyclic AMP signaling pathway, regulates cell cycle progression in primary melanoma cells. These data show differential role of EPAC in primary and metastatic melanoma cells and provide a basis for targeting EPAC for prevention of cutaneous melanoma progression.Ĭitation Format: Aishwarya Krishnan, Kirthana Prabhakar, Mary Ndiaye, Nihal Ahmad, Carlos Ivan Rodriguez, Vijayasaradhi Setaluri. Inhibition of EPAC in metastatic melanoma cells, on the other hand, stimulated their growth. Paradoxically, inhibition of EPAC also caused an increase in AKT phosphorylation, suggesting a cell survival response elicited upon the cell cycle arrest caused by inhibition of EPAC allows continued survival of primary melanoma cells. Flow cytometry and western blot analysis of cell cycle proteins showed that inhibition of EPAC arrests cells in G1-S and delays their mitotic progression. In this study, we show that pharmacological inhibition of EPAC, delays cell cycle progression and inhibits the growth of human primary melanoma cells. Exchange Protein directly Activated by cAMP (EPAC) constitutes an alternative pathway to cAMP signaling and is known to mediate the crosstalk between the cAMP and MAPK pathways. Despite the importance of cAMP signaling in melanocytes, very little is known about its role in melanoma. Polymorphisms in MC1R lead to cAMP signaling impairments which are accompanied by higher risk for melanoma development.

In melanocytes, the G-Protein Coupled Receptor (GPCR) Melanocortin-1-Receptor (MC1R), an important regulator of melanocyte proliferation and melanogenesis, activates cAMP signaling. Cyclic AMP (cAMP) is an important second messenger that acts as a key mediator in a wide range of cellular pathways.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
